Easily Build a Scalable Web Application in Go

I’m Jay RealBuckSavage, a lead software engineer at Sarvika Technologies, and I’m gonna show y’all how you can easily build scalable web applications in Go.
Why I LOVE Go
I’ve been in software development for a long time. I started out as a hobbyist, writing
mods for GoldSrc and Source game engines by Valve. Later I turned towards writing desktop and network based
programs, and now I’m writing web applications for businesses having massive scale at Sarvika.
During this time, I’ve had so many brutal death battles with a lot
of server-side languages like Java, Scala, Kotlin, Ruby, and
Python. I started working with Go a few months ago and boy I’m sold. Here’s why I love
Go.
- Easy everything: Go applications are easy to understand and
write, and I just can’t stop loving the dependency management system.Proofreaders will miss this
text - Fast: Go code compiles fast, and it runs fast. Let’s admit that
we don’t like to wait for a build process to finish! - Efficient: Since Go code is easy to understand, it’s fairly easy
to write our own. Go allows you to be productive instead of putting time into things like deciding what
package your class should go in. - Gophers!:
At least it’s not an ugly mug of coffee…
Getting our hands dirty
We’ve had our share of chitchat, now to write some code. I’m assuming that you already
have Go installed on your machine and know about Go‘s directory structure. Also, I’m using
Archlinux (btw) to write all code for this blog post, if that matters.
This project is available on my GitHub (since I’m not going to put out each line of
code in this post).
Libraries & Tools I’ll be using
Setting up the project
$ GH_USER=realbucksavage
$ mkdir -p $(go env GOPATH)/github.com/${GH_USER}/todos
$ cd $(go env GOPATH)/github.com/${GH_USER}/todos
$ go get github.com/gin-gonic/gin
$ go get github.com/jinzhu/gorm
Be sure to replace
GH_USERwith your GitHub username. I’m using realbucksavage since that’s
what I have.
Getting started
A very basic Gin app looks
like this:
package main
import "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/ping", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(200, gin.H{
"message": "pong",
})
})
if err := r.Run(":8080"); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
Gin provides us with an easy to understand routing mechanism. This snippet
is giving an insight of what we’re dealing with. You can go ahead and run this program and do a quick
curl --silent localhost:8080/ping | jq . to look at our pretty JSON response.
But this is not enough for what we need. It’s a working program but we need
something more, so we’ll refactor. This is how the project ended up looking like by the time I completed it.
.
├── api
│ ├── api.go
│ └── todos
│ ├── todos.ctrl.go
│ └── todos.go
├── database
│ ├── database.go
│ ├── inject.go
│ └── models
│ ├── migrate.go
│ └── todo.go
├── docker-compose.yml
├── Dockerfile
├── Gopkg.lock
├── Gopkg.toml
├── lib
│ ├── common
│ │ └── json.go
│ └── utils.go
├── main.go
└── README.md
Setting up routes
I like to divide my implementations in their own packages and let these packages
register their own routes. So I’m going to create a package api and let it register all routes to
/api. Also, there’s going to be a subpackage todos to handle all routes to
/api/todos.
Inspired by this GCUK talk.
// From api/api.go
func ApplyRoutes(r *gin.Engine) {
todosRoute := r.Group("/api")
todos.ApplyRoutes(todosRoute)
}
// From api/todos/todos.go
func ApplyRoutes(r *gin.RouterGroup) {
api := r.Group("/todos")
{
api.POST("/", create)
api.GET("/", list)
api.GET("/:id", get)
api.DELETE("/:id", remove)
api.PATCH("/:id", update)
}
}
Nice and easy. create, list, get,
remove, and update functions are declared in api/todos/todos.ctrl.go. I like
to call them controller functions, and that’s where this naming convention is coming from. Can’t blame me,
I’m still a Java boi at core ?
I’m not putting these functions in this post for obvious reasons, but you can check the
Github Repo out.
Setting up the database layer
So we have our app’s skeleton ready. I like to introduce a DB layer at this time.
// From database/database.go
func InitDb() *gorm.DB {
dbConfig := "sslmode=disable host=db port=5432 dbname=todos user=tduser password=tdpass"
db, err := gorm.Open("postgres", dbConfig)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
db.LogMode(true)
models.RunMigrations(db)
return db
}
Easy as that, but we still need to pass this DB reference to our controller
functions. We’ll use a simple middleware for that. And now that everything else is in place, we will
modify main.go as well.
// From database/inject.go
func Inject(db *gorm.DB) gin.HandlerFunc {
return func(c *gin.Context) {
c.Set("db", db)
c.Next()
}
}
// main.go
func main() {
db, _ := database.InitDb()
r := gin.Default()
// Apply the middleware that injects DB reference.
r.Use(database.Inject(db))
api.ApplyRoutes(r)
if err := r.Run(":8080"); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Cannot start server: %v\n", err)
}
}
And now, the controller functions can use the database connection like
this:
func list(c *gin.Context) {
db := c.MustGet("db").(*gorm.DB)
// ...
}
Build and run
This application is now ready to be built and run. I’ll use docker and
docker-compose to do this job since we have a dependency on a postgres database server.
Also, we will need to vendor this app before we containerize it. For this, I’ll use godep.
$ dep init
$ dep ensure
Now, to containerize, I’ll lay down my Dockerfile like this:
FROM golang:1.13-alpine
EXPOSE 8080
ENV GOPATH=/go
RUN mkdir -p $GOPATH/src/github.com/realbucksavage/todos
COPY . $GOPATH/src/github.com/realbucksavage/todos
WORKDIR $GOPATH/src/github.com/realbucksavage/todos
RUN go build -o todos .
CMD ["/go/src/github.com/realbucksavage/todos/todos"]
And docker-compse.yml like this:
version: '3' services: db: container_name: todosdb hostname: db image: postgres environment: POSTGRES_USER: tduser POSTGRES_PASSWORD: tdpass POSTGRES_DB: todos app: image: todosapi container_name: todosapi build: context: . dockerfile: Dockerfile ports: - 8080:8080 depends_on:- db
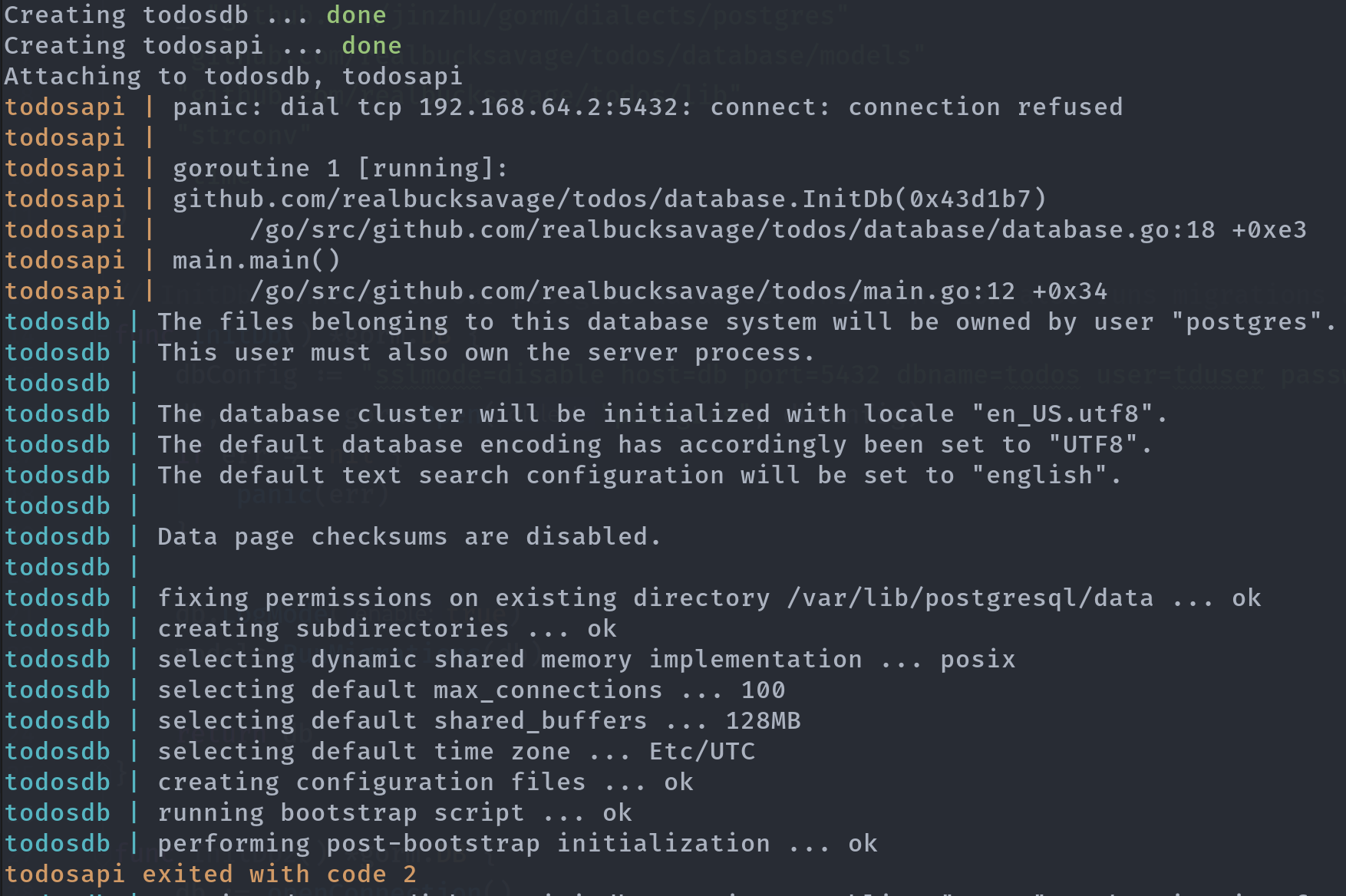
Great! Now let’s do a quick docker-compose up to see what happens.
The application’s container crashed because it attempted to connect to
postgres while it was still starting up. This means that we’ll have to implement a mechanism to attempt
a connection only when our database comes up as healthy. In the earlier versions of compose, the
depends_on parameter could be configured to check a container’s health status, but it has been removed
in version 3. Great, now we’ll have to improvise.
To cope up with this, I implemented a lazy mechanism in database.go that
keeps on trying to make a connection to the database for a limited number of times before letting the app to crash.
func InitDb() *gorm.DB {
db := openConnection()
db.LogMode(true)
models.RunMigrations(db)
return db
}
func openConnection() *gorm.DB {
maxRetries := 3
waitTime := 5 // In seconds
for i := 1; i <= maxRetries; i++ {
fmt.Printf("Opening Connection; Attempt %d of %d...\n", i, maxRetries)
dbConfig := "sslmode=disable host=db port=5432 dbname=todos user=tduser password=tdpass"
db, err := gorm.Open("postgres", dbConfig)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Cannot open connection (retrying in %ds): %v\n", waitTime, err)
time.Sleep(time.Duration(waitTime) * time.Second)
continue
}
return db
}
panic(fmt.Errorf("Cannot open database connection after %d retries!\n", maxRetries))
}
Let’s try again.
$ docker-compose build && docker-compose up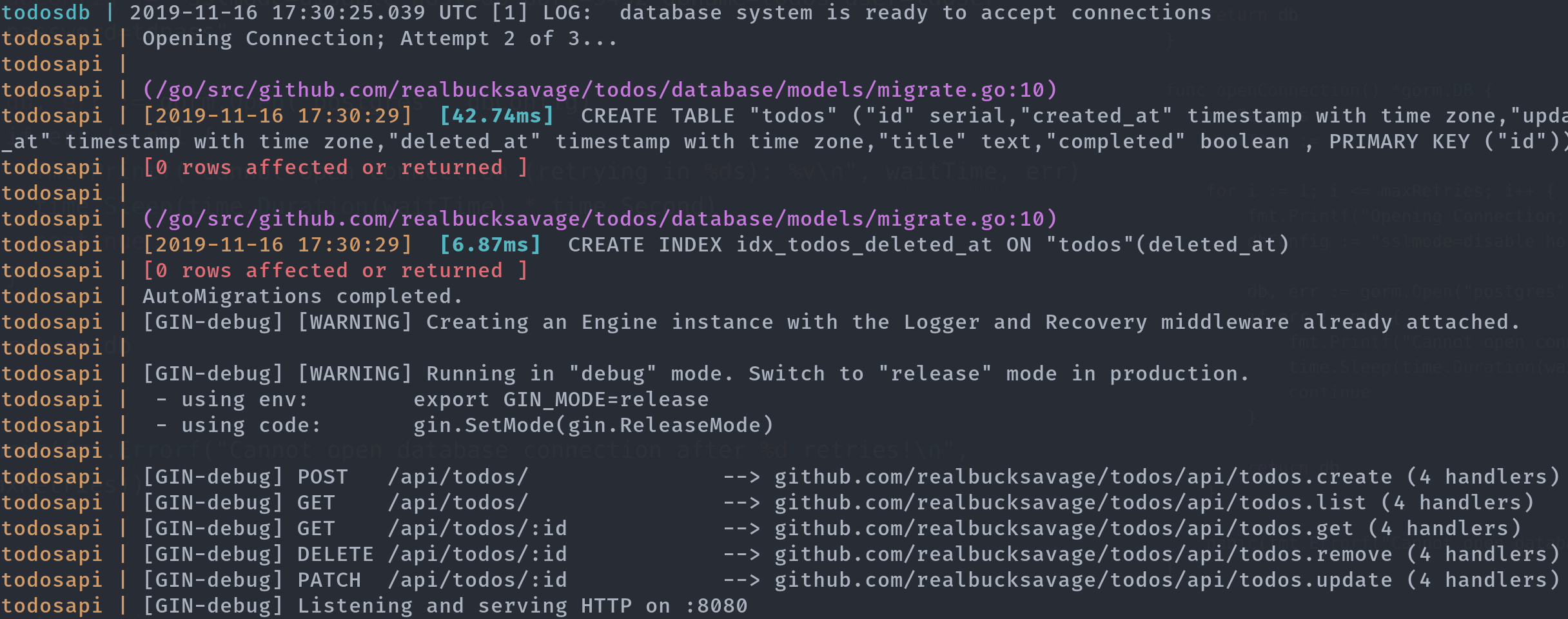
Aaaaaaaaaaand it worked.
So we have a simple REST API server implemented in Go, but there’s
still a lot more to do before we can spin this up in production. Also, there will be more parts coming up soon.
Subscribe to Sarvika’s newsletter to stay tuned and see more content from us 🙂
The source code for this project is available on GitHub. If you see anything out of place or wish to
improve something, please submit a PR or use the issues board to contact me.
Thanks for reading, here’s a gopher eating sweet potato.






 Branded Solutions
Branded Solutions